Earth
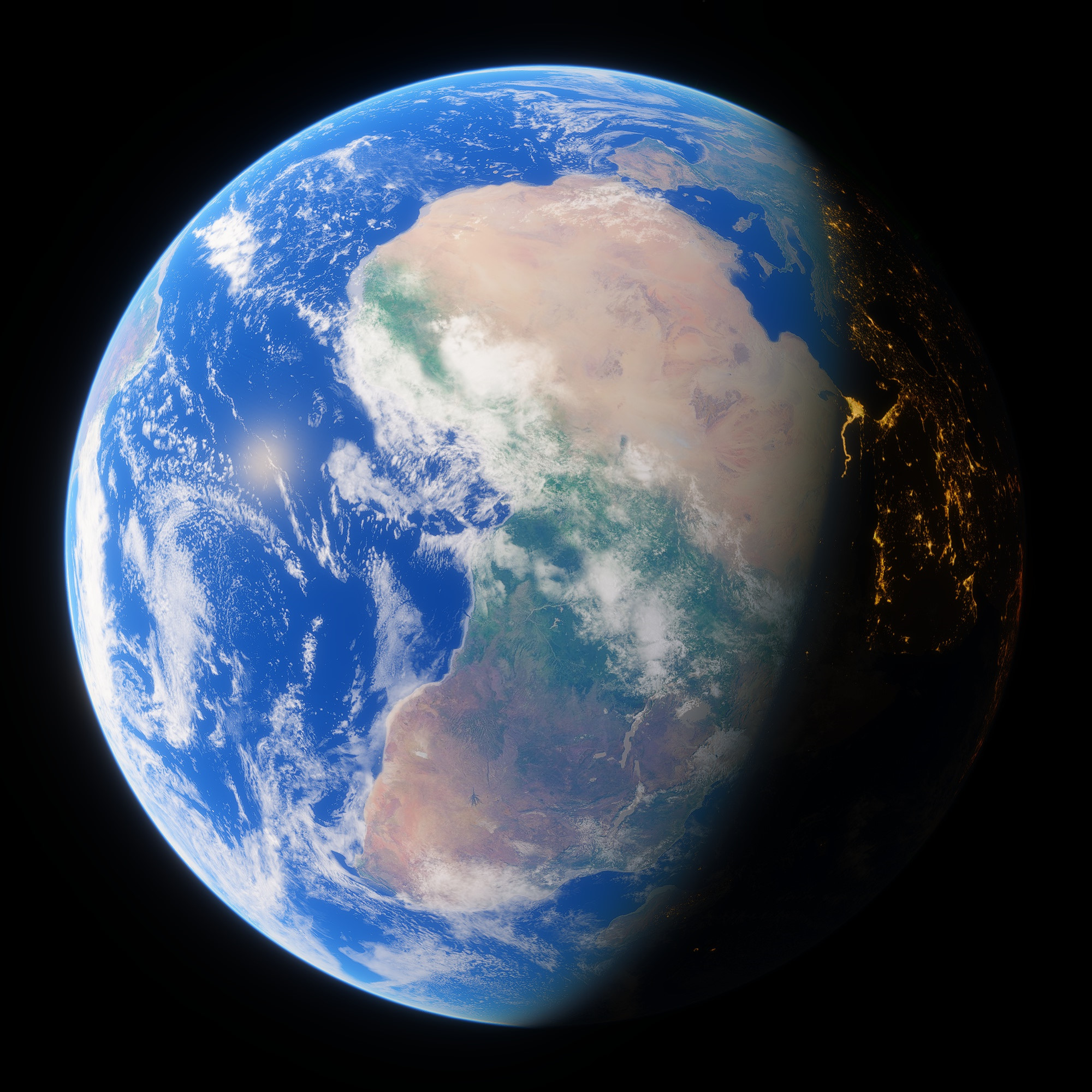
The planet Earth is a vibrant terran world in the Sol system with a diverse biosphere recovering from a near-miss ecological collapse. Being the only tectonically active planet in the Sol system and one of two worlds in the system with liquid surface water, Earth is the archetype of the terran planetary class. Earth is home to an indigenous sophont species: humans. It is roughly the center of known space and the United Nations Aerospace Commission's primary center of operations, making it cartographically critical to the interstellar network. It is one of a minority of worlds divided into nations, hence its primary governing body being the United Nations of Earth -the ancestor to most of humankind's modern administrative structure.
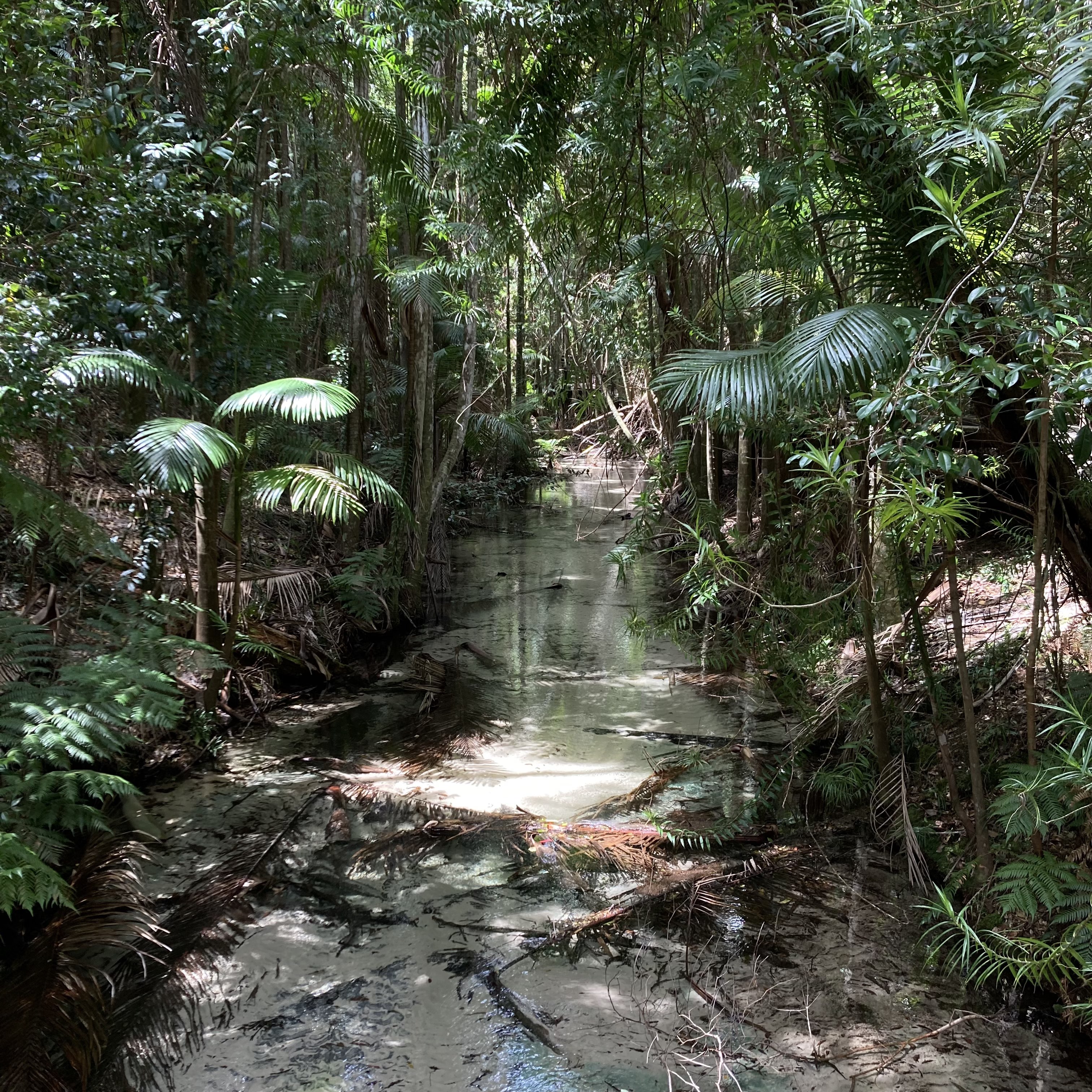
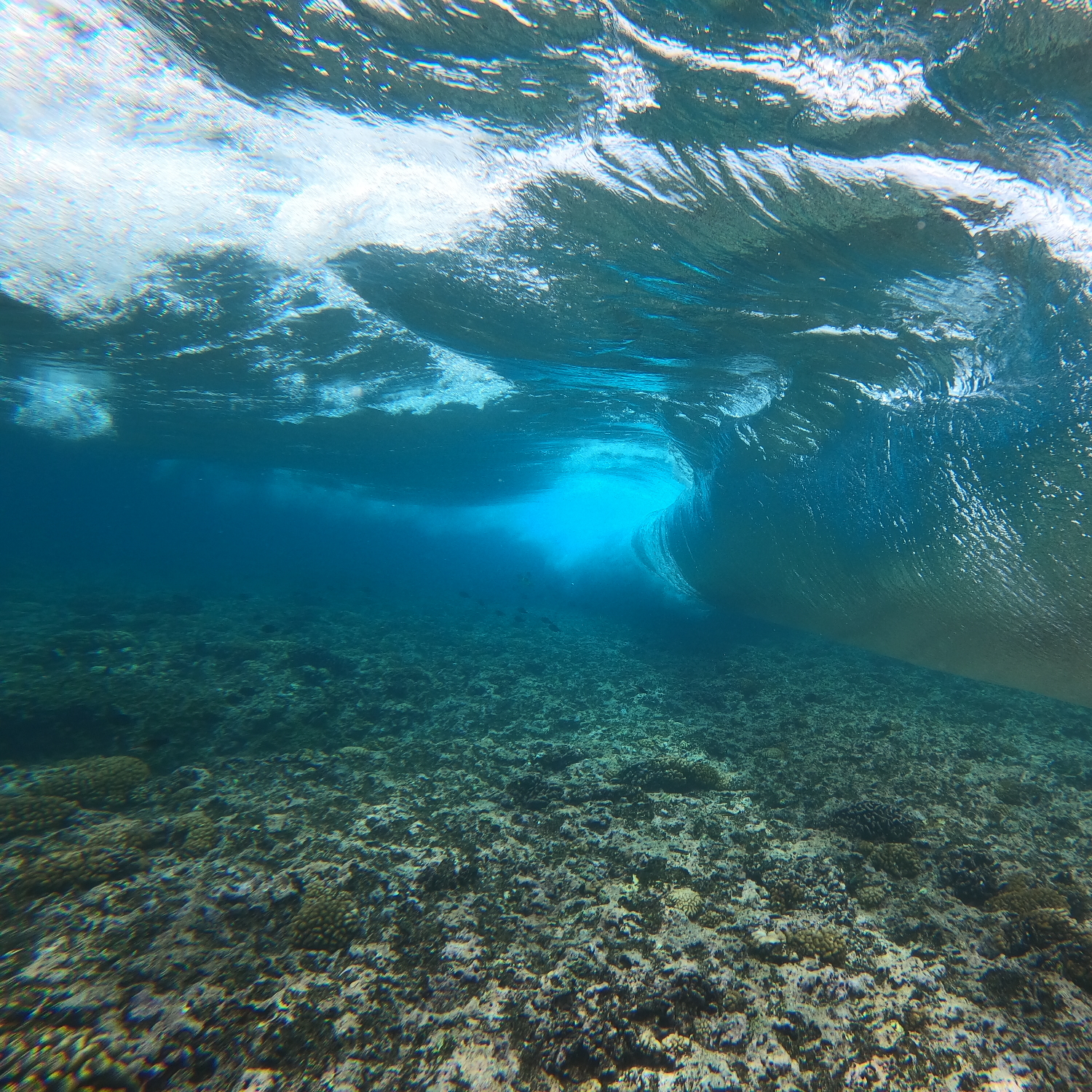
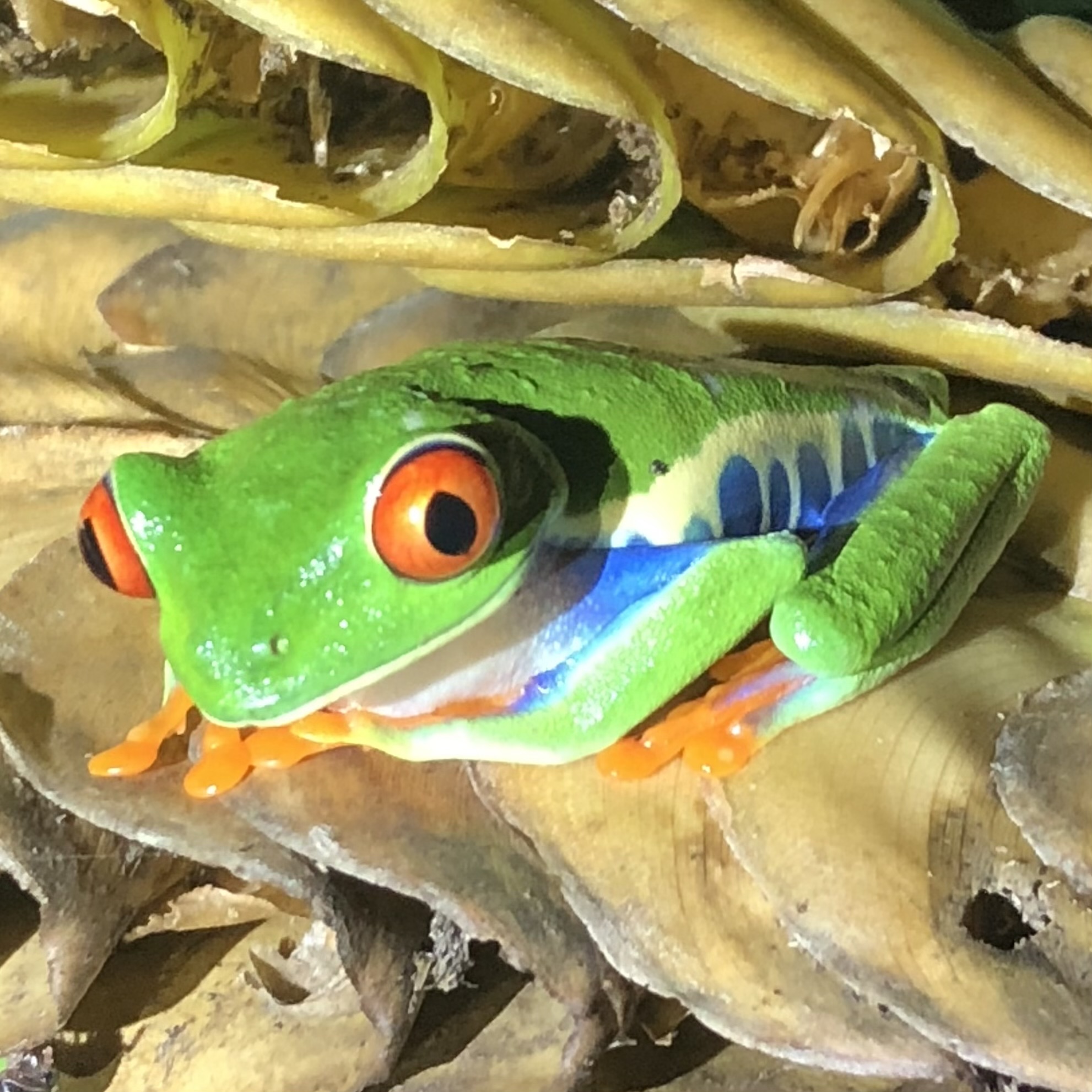
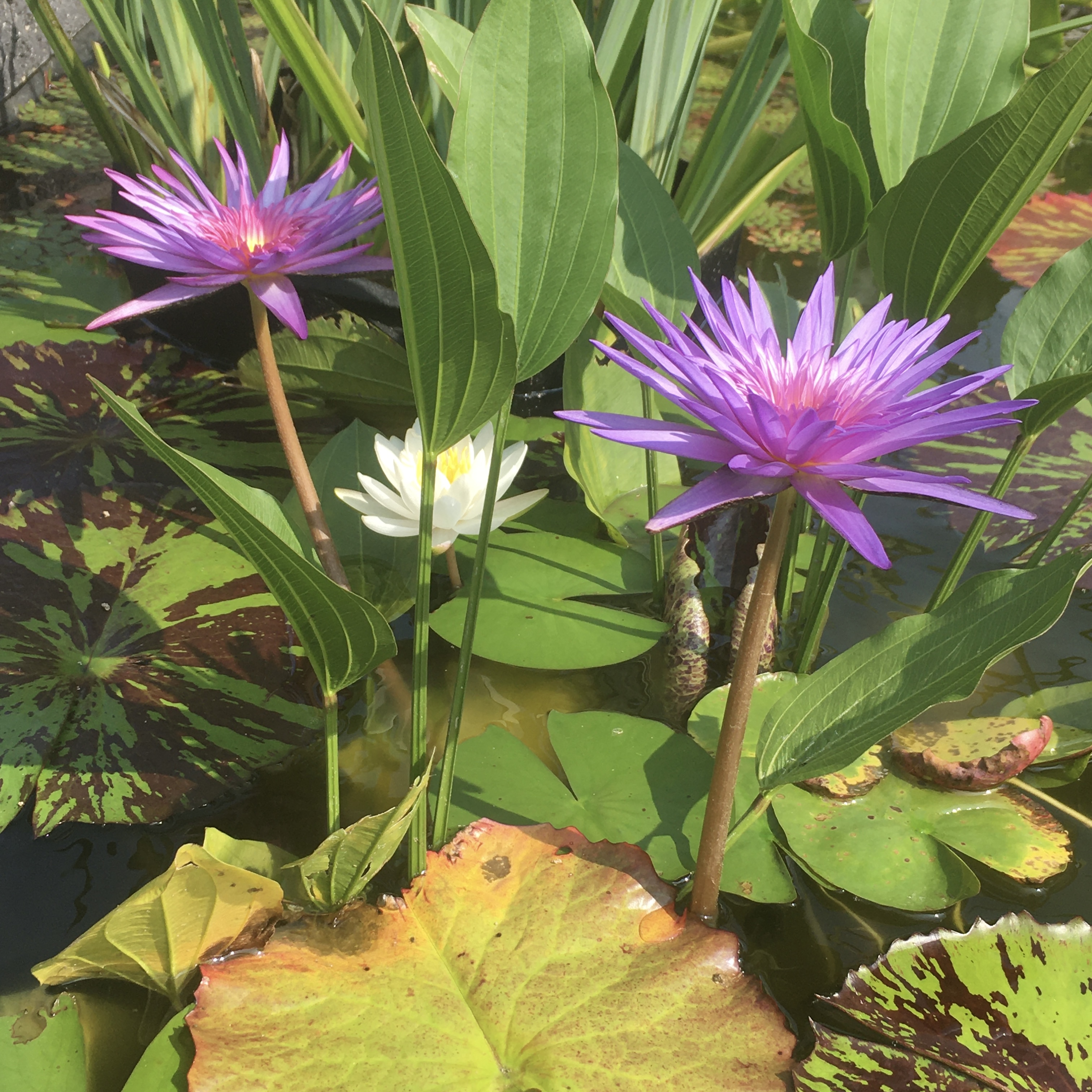
Earth’s rich cultural and biological history makes it a tourist destination renowned across known space, despite the strict biosecurity procedures. For many humans, it is even a spiritual experience, making it their life’s goal to retire on Earth and connect with the home of their ancestors. Centuries of ecological engineering and conservation have managed to avert the effects of early human industry, restoring the world to a natural balance and even reviving many species driven extinct by human error. Today, one can watch herds of mammoth roam the Siberian tundra, visit dodo birds on Mauritius, or experience the return of Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. 30th century Earth is a good place to be, and humanity is collectively proud of their home: the cradle of the diaspora.
Geography
Location
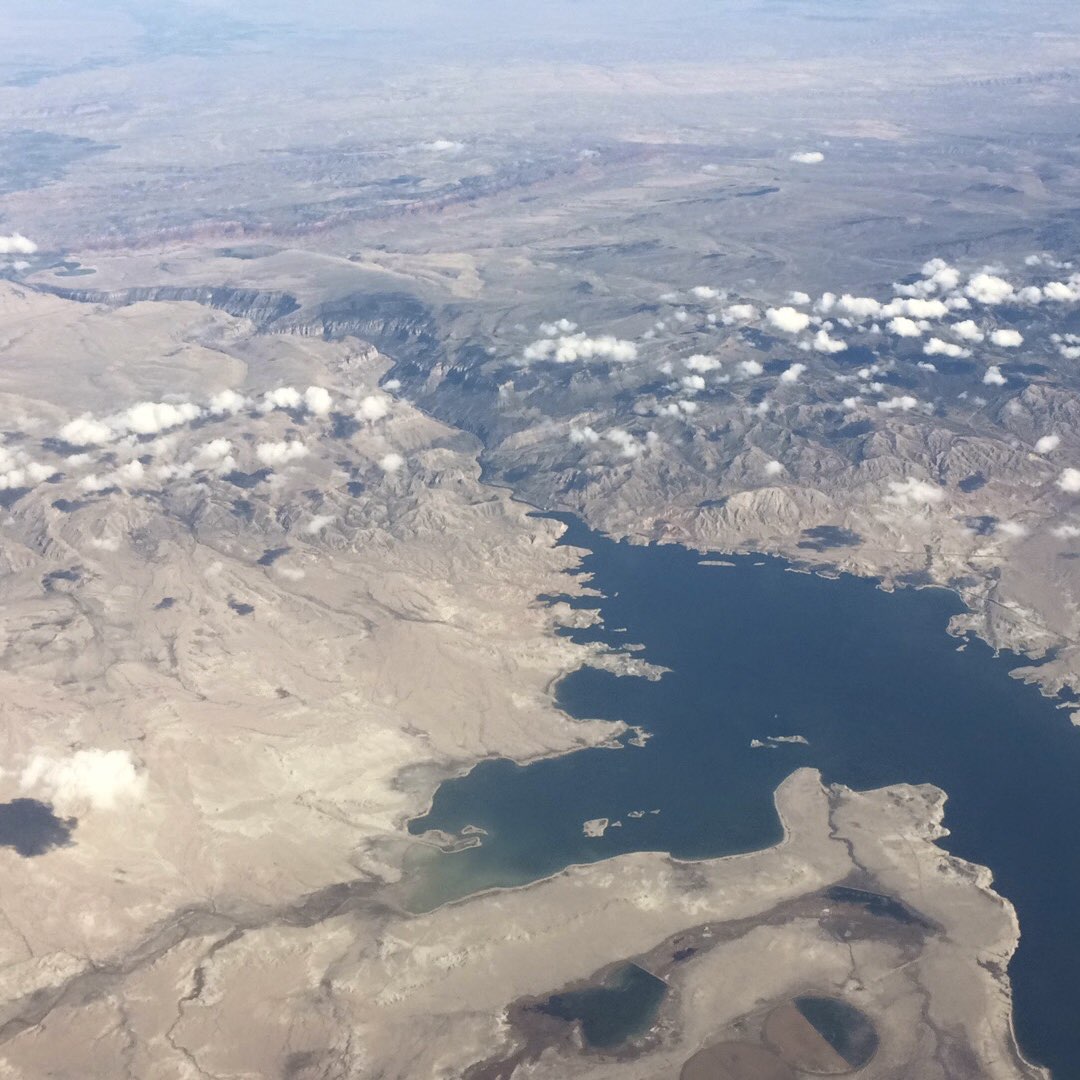
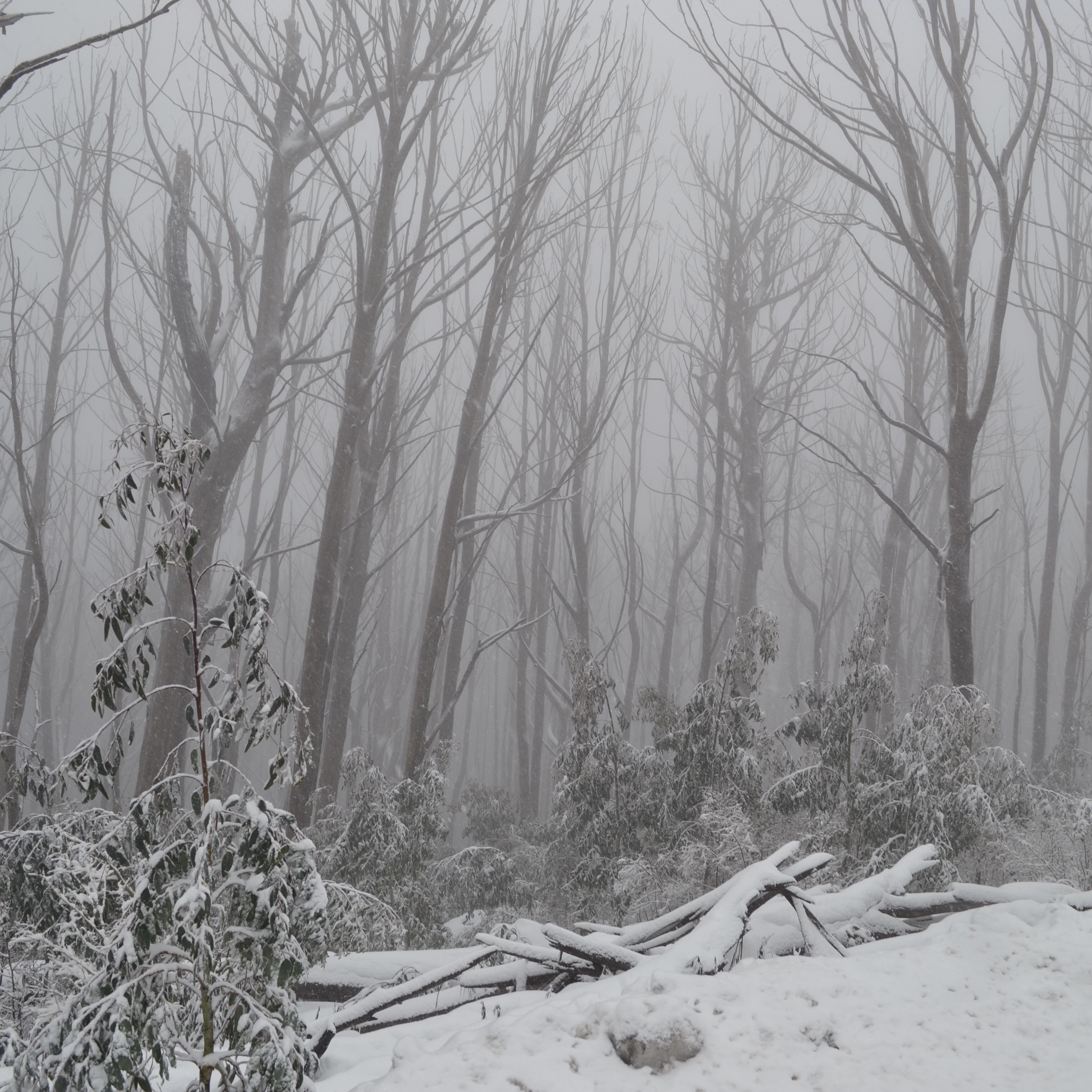
Surface
Click this image to view an interactive 3D map of Earth.
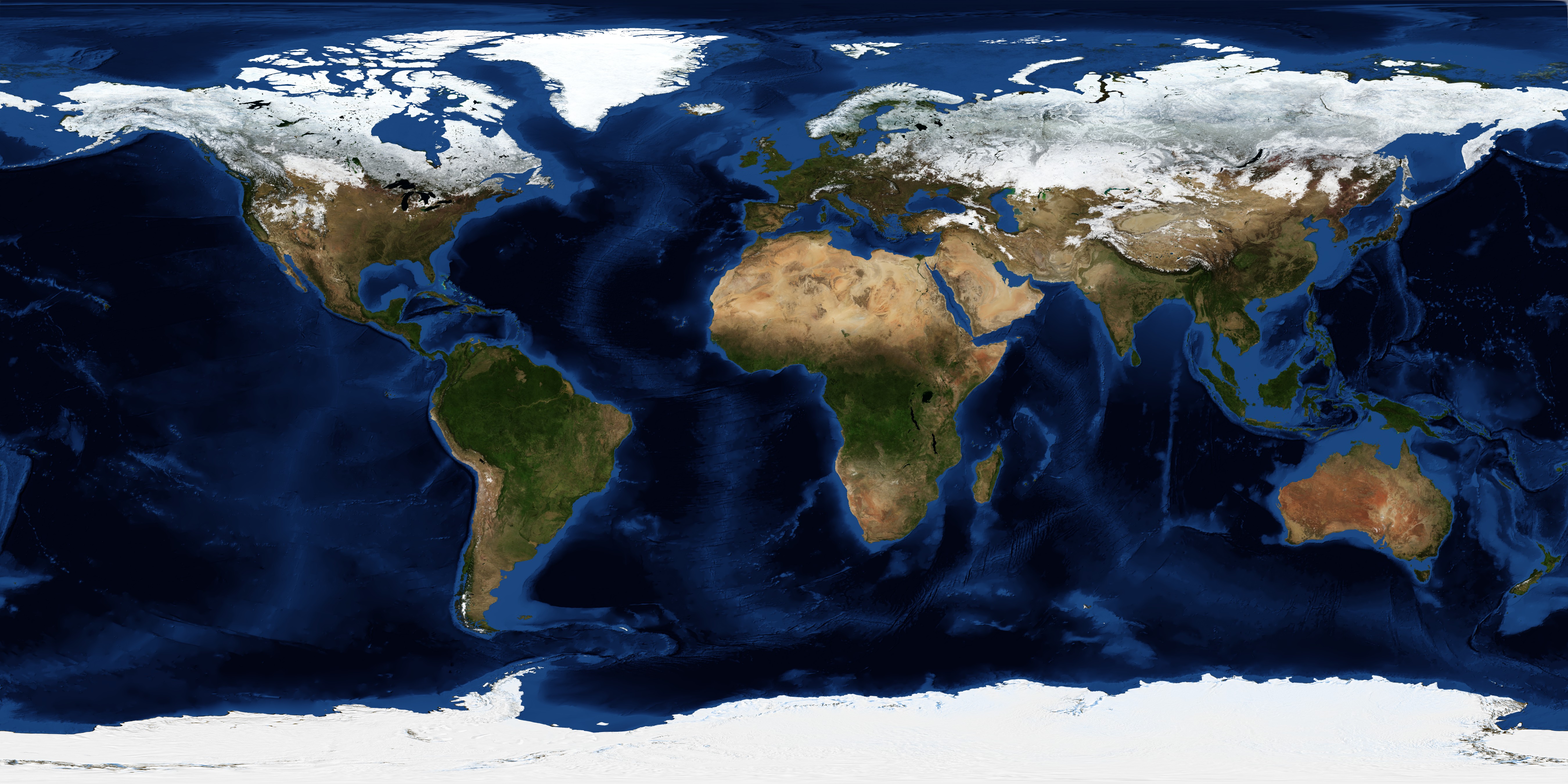
by NASA (Earth Observatory)
For more information, visit the Wikipedia page on Earth.
Ecosystem
Resources & Industry
For a significant portion of human history, Earthly civilization's primary source of energy was combustion of geologically-condensed hydrocarbons: so-called "fossil fuels." However, this mode of power quickly destabilized the global climate, resulting in a mass shift into a combination of renewable-environmental and nuclear energy in the early 21st century. During the environmental reclamation of the next several centuries, almost all industry was moved offworld; either into low orbit or to Luna. The vast, incredibly destructive farming practices of the 20th century have been replaced by responsible biomass management planning. Earthlings eat what they can grow, catch, or more commonly print, leaving most of the surface of the planet to become wild again - at least, wild with human oversight. In the modern day, the dominant percentage of the work that remains Earthbound deals with biology: genetic archiving and export, ecological management, or, yes, even ecotourism. Due to Earth's status as one of a very small number of worlds in the universe with a truly indigenous and well-established biosphere, the planet has strict self-imposed restrictions on mass exportation. However, this rare and extremely high level of biodiversity allows Earth's primary natural resource to be genetic information, exported either via pure data, tissue samples, or genetic material isolate samples.Earth from orbit, with city lights visible across central Eurasia and northern Africa.
Archive Data
HAZARDS
- 78% nitrogen
- 21% oxygen
- 0.9% argon
- 0.1% other gases
Inhabitants
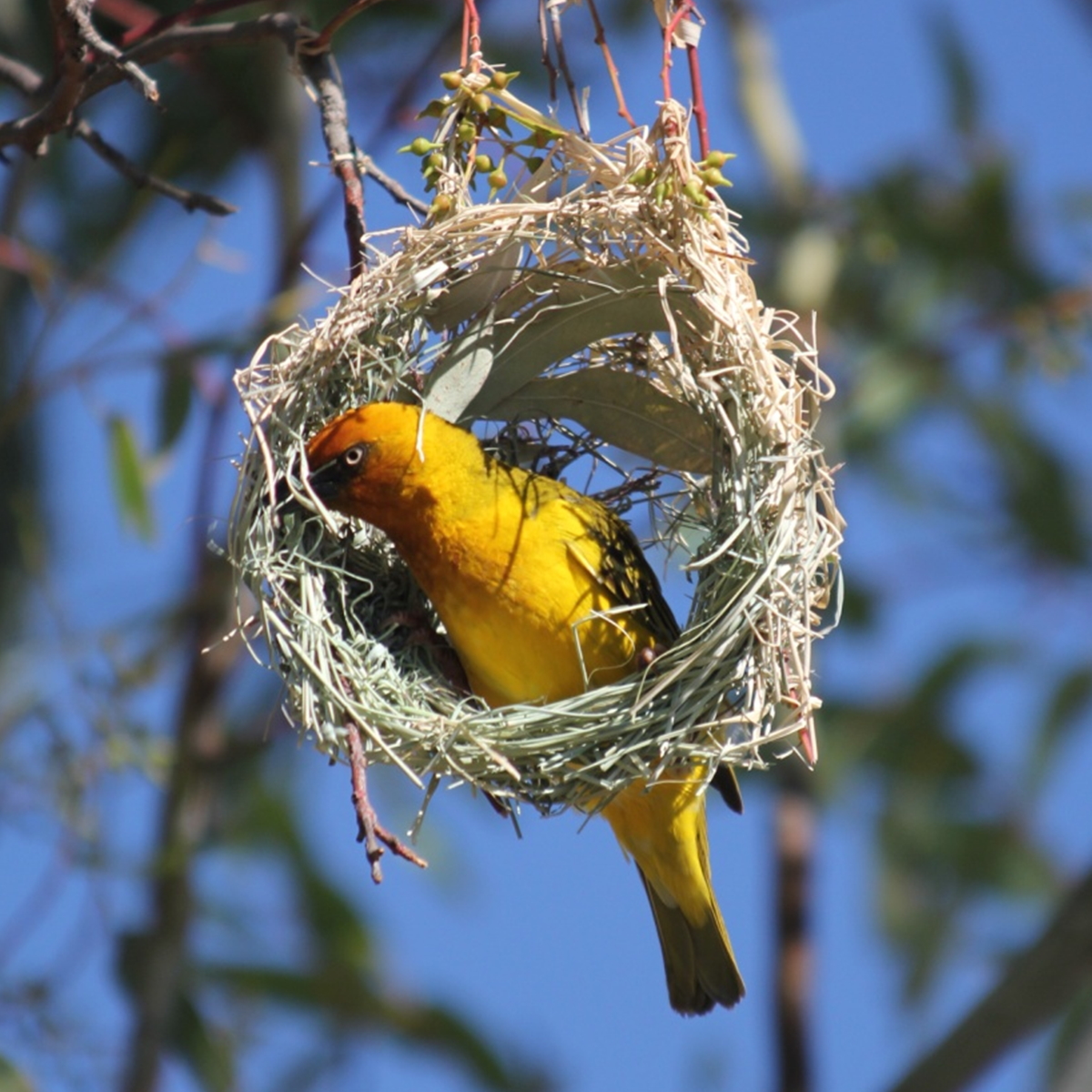
Earth is inhabited by two confirmed sophont species, only one of which has achieved technological civilization. Humans (depicted above) thought themselves the sole sapient inhabitants of Earth for most of their history. However, in the mid-22nd century they were finally able to communicate intelligibly with the other sophonts of their planet: orca whales. Since then, biologists have come to the conclusion that multiple different genera of organisms on Earth exhibit the evolutionary trend toward sapience, including corvids, pachyderms, and octopi.Biosecurity
Earthlings have spent the last several centuries repairing the biosphere they accidentally broke, and take ecological defense and maintenance incredibly seriously. Earth may be dependent on manufactured goods from its orbital space and moon, but there is a mandatory 48-hour quarantine and screening process in place for all crewed vessels attempting a landing, and mandatory sterilization for uncrewed spacecraft. While supplementary artificial immune systems are standard across the whole UNH and spaceflight itself acts as a long-term quarantine, the people of Earth are not taking chances on their planetary biosphere.Terragenia
Chemistry
- Hydrogen
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorous
- Sulfur
Metabolics
- Nicotinamide reversible hydrogen ionization
- Acetyl enzyme oxidation
Genetics
- Adenine
- Cytosine
- Guanine
- Thymine
- Uracil



















Comments